Enamine To Carbonyl Mechanism

Enamine To Carbonyl Mechanism. Enamines are formed by the reaction of secondary amines with carbonyl compounds. Is imine the e or nu in nucleophilic addition. There are two simple classes of the carbonyl group: Like imine formation, enamine formation is reversible, and enamines can be coaverted back to the corresponding carbonyl compounds. Various examples and reaction conditions were studied keywords: The mechanism most likely involves conjugate addition of the enamine tautomer of the bicyclic imine followed by closure to the lactam, as attempts. Enamine alkylation (18.6c) stork enamine reaction dialkylation. In this post we go into the synthesis of imines and enamines and the mechanism of imine formation. Proton transfer to the base. Under the appropriate conditions, secondary amines react with carbonyl compounds to form enamines. In this screencast we examine the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of an enamine to a ketone and a this video describes the reaction of a carbonyl compound with a secondary amine to yield an enamine.
◀ ←video lecture 95 of 143→ ▶. The enamine form of the product is analogues to the enolate form of the carbonyl compound. If substituent y is a hydrogen, an alkyl group or an aryl group, the resulting alcohol is a stable compound and does not decompose with. Enamines are similar to enols and enolates in that they also undergo alpha substitution reactions. Enol form of the carbonyl compound (18.1c) enol forms of carbonyl compounds, as well as the carbonyl compound, are in equilibria with enolate ions. The carbonyl group is a polar functional group that is made up a carbon and oxygen double bonded together.
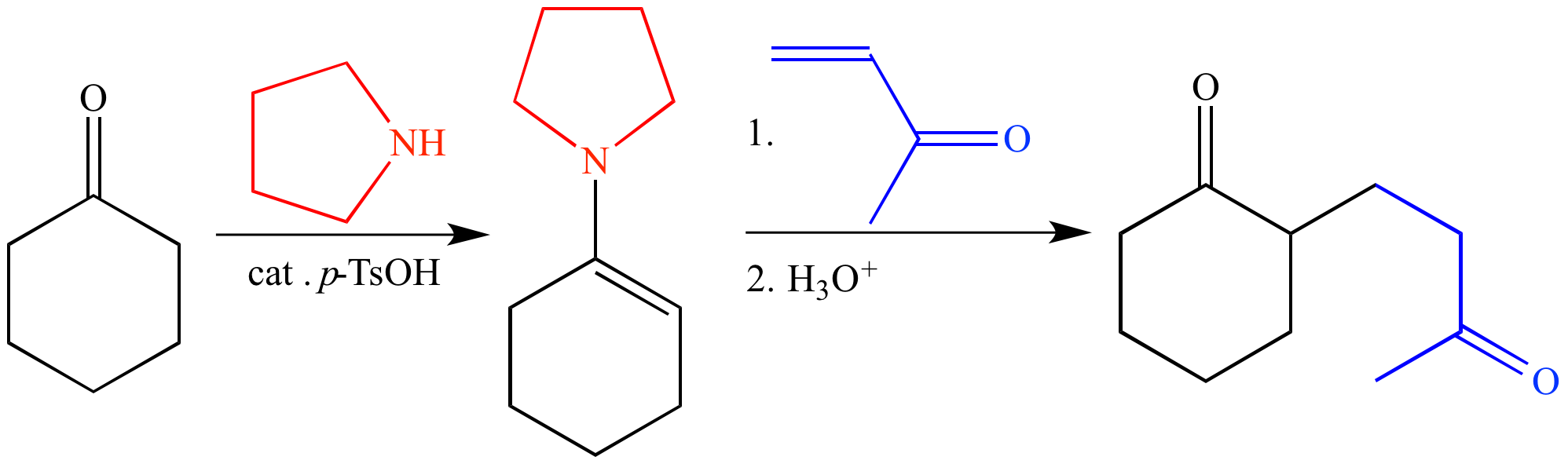
The mechanism most likely involves conjugate addition of the enamine tautomer of the bicyclic imine followed by closure to the lactam, as attempts.
The resulting intermediate is now very electrophilic and the c=o carbon is attacked by water forming an unstable tetrahedral intermediate. The mechanism of intramolecular aldol reactions is similar to that of intermolecular reactions. The mechanism is given in chapter 14. Is imine the e or nu in nucleophilic addition. ◀ ←video lecture 95 of 143→ ▶. Mechanism of the proline catalyzed aldol cyclization is best described by the nucleophilic addition of the neutral enamine to the carbonyl group together. Enamines are similar to enols and enolates in that they also undergo alpha substitution reactions. Interactive 3d animations and modelsof enamine formation from an amine and an aldehyde for students studying university chemistry. They are made when aldehydes and ketones react with secondary amines. Acid catalysed hydration of an aldehyde. In this post we go into the synthesis of imines and enamines and the mechanism of imine formation. But once again the mechanism is the same until. Enol form of the carbonyl compound (18.1c) enol forms of carbonyl compounds, as well as the carbonyl compound, are in equilibria with enolate ions. There are two simple classes of the carbonyl group:
Reactions of enamines as nucleophiles sn2 an iminium salt hydrolysis alkylation. The enamine form of the product is analogues to the enolate form of the carbonyl compound. The overall process, from carbonyl compound to carbonyl compound, amounts to an enolate alkylation, but no strong base or enolates are involved so there is no danger of. The process of performing a carbonyl alpha substitution reaction via an in the mechanism below the carbonyl was deprotonated at the alpha position, and the enolate was then drawn as a resonance form. Enamines are the nitrogen analogues of enols. The mechanisms illustrate why the reaction of 1° amines with carbonyl compounds forms imines, but the reaction with 2° amines forms enamines. Enamines and enols are structural analogs.

Nucleophilic character of enamines c nucleophilic at carbon x sn2.
Enamines are similar to enols and enolates in that they also undergo alpha substitution reactions. Is imine the e or nu in nucleophilic addition. But first let us take a look at the mechanism of formation of these imines and enamines. In this post we go into the synthesis of imines and enamines and the mechanism of imine formation. In this screencast we examine the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of an enamine to a ketone and a this video describes the reaction of a carbonyl compound with a secondary amine to yield an enamine. The overall process, from carbonyl compound to carbonyl compound, amounts to an enolate alkylation, but no strong base or enolates are involved so there is no danger of. The mechanism most likely involves conjugate addition of the enamine tautomer of the bicyclic imine followed by closure to the lactam, as attempts. The mechanism of formation of hemiacetal is analogob to that of the. Enamine alkylation (18.6c) stork enamine reaction dialkylation. In the stork reaction, for example, an enamine adds to. Reactions of enamines as nucleophiles sn2 an iminium salt hydrolysis alkylation. The mechanism of intramolecular aldol reactions is similar to that of intermolecular reactions.
The mechanism of intramolecular aldol reactions is similar to that of intermolecular reactions. They are made when aldehydes and ketones react with secondary amines. Mechanism of the proline catalyzed aldol cyclization is best described by the nucleophilic addition of the neutral enamine to the carbonyl group together. Proton transfer to the base. Acid catalysed hydration of an aldehyde. In this screencast we examine the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of an enamine to a ketone and a this video describes the reaction of a carbonyl compound with a secondary amine to yield an enamine. Reactions of enamines as nucleophiles sn2 an iminium salt hydrolysis alkylation. By comparing the exchange reactions between pairs (enamine a + carbonyl b → carbonyl a + enamine b), a quite general scale of the tendency of.
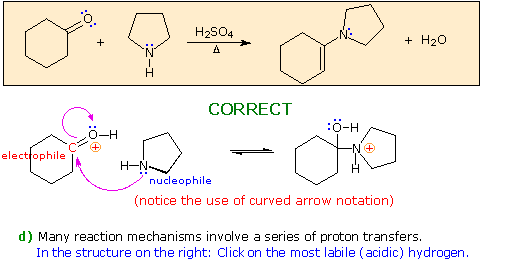
Enamines and enols are structural analogs.
Acid catalysed hydration of an aldehyde. Leaving group conversions hx 7. The overall process, from carbonyl compound to carbonyl compound, amounts to an enolate alkylation, but no strong base or enolates are involved so there is no danger of. Mechanism of the proline catalyzed aldol cyclization is best described by the nucleophilic addition of the neutral enamine to the carbonyl group together. Enamines are formed when aldehydes or ketones react with secondary amines. The carbonyl group is a polar functional group that is made up a carbon and oxygen double bonded together. The mechanism is given in chapter 14. And then your carbonyl oxygen is going to be protonated. Enol form of the carbonyl compound (18.1c) enol forms of carbonyl compounds, as well as the carbonyl compound, are in equilibria with enolate ions. Reactions of enamines as nucleophiles sn2 an iminium salt hydrolysis alkylation. Is imine the e or nu in nucleophilic addition. Enamines are formed by the reaction of secondary amines with carbonyl compounds.
The mechanism of enamine formation begins, like the mechanism of imine formation, as a enamine mechanism. Enamines are formed when aldehydes or ketones react with secondary amines.
 Source: media.springernature.com
Source: media.springernature.com Mechanism of enamine formation from ketones or aldehydes with secondary amines.
 Source: i.pinimg.com
Source: i.pinimg.com Interactive 3d animations and modelsof enamine formation from an amine and an aldehyde for students studying university chemistry.
 Source: media.springernature.com
Source: media.springernature.com Enamine alkylation (18.6c) stork enamine reaction dialkylation.
 Source: pubs.rsc.org
Source: pubs.rsc.org The carbonyl group is a polar functional group that is made up a carbon and oxygen double bonded together.
 Source: pharmaxchange.info
Source: pharmaxchange.info Enamines are formed when aldehydes or ketones react with secondary amines.
 Source: i.ytimg.com
Source: i.ytimg.com Enamines are an important specific enol equivalent.
 Source: useruploads.socratic.org
Source: useruploads.socratic.org But once again the mechanism is the same until.
 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org The mechanism of formation of hemiacetal is analogob to that of the.
 Source: images.ctfassets.net
Source: images.ctfassets.net The only difference is that both the nucleophilic carbonyl enamines are electronically similar to enolate ions and behave in the same way as enolate ions.
 Source: www.mdpi.com
Source: www.mdpi.com But first let us take a look at the mechanism of formation of these imines and enamines.
 Source: www.scielo.br
Source: www.scielo.br Leaving group conversions hx 7.
 Source: pubs.rsc.org
Source: pubs.rsc.org The mechanisms illustrate why the reaction of 1° amines with carbonyl compounds forms imines, but the reaction with 2° amines forms enamines.
 Source: www.pnas.org
Source: www.pnas.org The mechanism is given in chapter 14.
 Source: i.ytimg.com
Source: i.ytimg.com Interactive 3d animations and modelsof enamine formation from an amine and an aldehyde for students studying university chemistry.
 Source: media.springernature.com
Source: media.springernature.com Mechanism of enamine formation from ketones or aldehydes with secondary amines.
 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org They are made when aldehydes and ketones react with secondary amines.
 Source: mk0chemistrysco84nst.kinstacdn.com
Source: mk0chemistrysco84nst.kinstacdn.com The resulting intermediate is now very electrophilic and the c=o carbon is attacked by water forming an unstable tetrahedral intermediate.
 Source: i.ytimg.com
Source: i.ytimg.com The mechanisms illustrate why the reaction of 1° amines with carbonyl compounds forms imines, but the reaction with 2° amines forms enamines.
 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org But first let us take a look at the mechanism of formation of these imines and enamines.
In this post we go into the synthesis of imines and enamines and the mechanism of imine formation.
 Source: useruploads.socratic.org
Source: useruploads.socratic.org The overall process, from carbonyl compound to carbonyl compound, amounts to an enolate alkylation, but no strong base or enolates are involved so there is no danger of.
 Source: cdn.masterorganicchemistry.com
Source: cdn.masterorganicchemistry.com Enamines are formed by the reaction of secondary amines with carbonyl compounds.
 Source: useruploads.socratic.org
Source: useruploads.socratic.org They are made when aldehydes and ketones react with secondary amines.
Mechanism of enamine formation from ketones or aldehydes with secondary amines.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com But once again the mechanism is the same until.
 Source: external-preview.redd.it
Source: external-preview.redd.it In this screencast we examine the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of an enamine to a ketone and a this video describes the reaction of a carbonyl compound with a secondary amine to yield an enamine.
 Source: media.springernature.com
Source: media.springernature.com The mechanism of formation of hemiacetal is analogob to that of the.
 Source: www.brainyresort.com
Source: www.brainyresort.com The mechanism most likely involves conjugate addition of the enamine tautomer of the bicyclic imine followed by closure to the lactam, as attempts.
 Source: upload.wikimedia.org
Source: upload.wikimedia.org In this post we go into the synthesis of imines and enamines and the mechanism of imine formation.
 Source: chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com Various examples and reaction conditions were studied keywords:
 Source: www.chemistrysteps.com
Source: www.chemistrysteps.com Interactive 3d animations and modelsof enamine formation from an amine and an aldehyde for students studying university chemistry.
 Source: www.brainyresort.com
Source: www.brainyresort.com Enamines are formed when aldehydes or ketones react with secondary amines.
Posting Komentar untuk "Enamine To Carbonyl Mechanism"